Cultivating your own vegetables at home is a rewarding experience, offering fresh produce, connection with nature, and a sense of accomplishment. This comprehensive guide walks you through every step, from initial planning to harvesting your bounty. Whether you have a small balcony or a spacious backyard, we’ll equip you with the knowledge and strategies to succeed.
From selecting the ideal location and appropriate vegetables to mastering planting techniques, soil preparation, and ongoing care, this guide provides practical advice. Discover the benefits of growing your own food, and learn how to create a thriving home garden, no matter your space constraints.
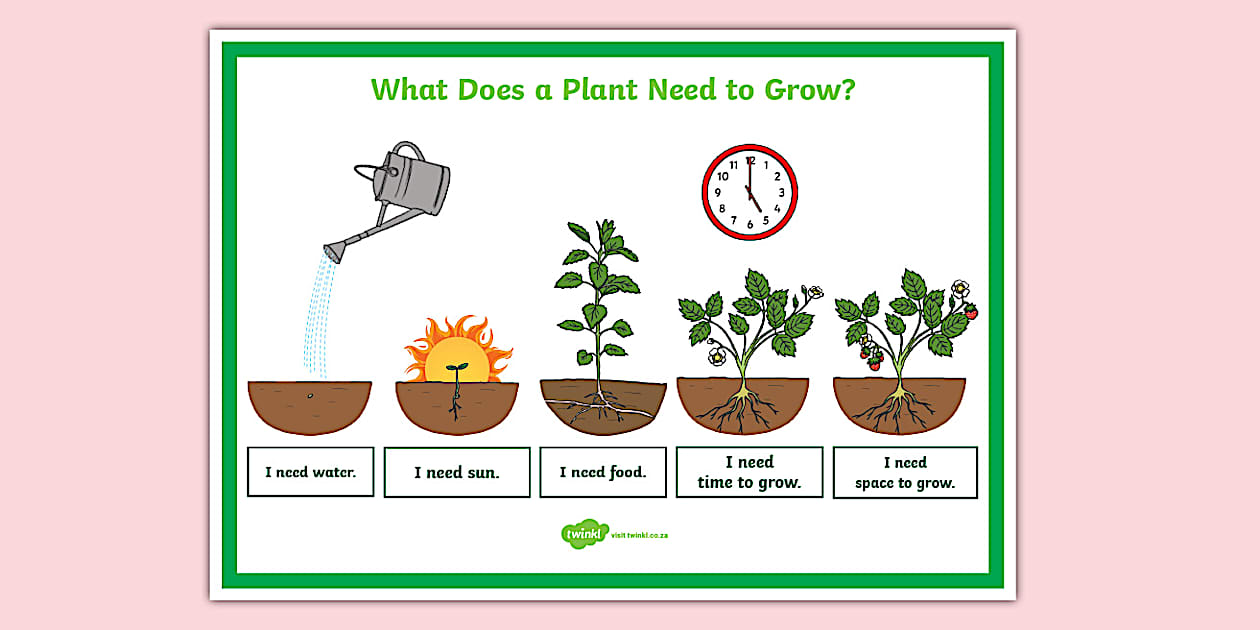
Introduction to Home Vegetable Gardening

Cultivating your own vegetables at home offers a rewarding experience, providing fresh, healthy produce while connecting you with the natural world. It’s a fantastic way to enhance your diet, reduce reliance on store-bought produce, and potentially save money. Beyond the practical benefits, home gardening fosters a sense of accomplishment and satisfaction.
Types of Home Vegetable Gardens
Home vegetable gardens come in diverse forms, each with its own advantages. Understanding the various types can help you choose the best fit for your space and needs. A thoughtfully planned garden can bring the freshest vegetables to your table.
- Raised Beds: These elevated structures offer excellent drainage and soil control. They are particularly useful for gardeners with limited space or challenging soil conditions. Raised beds are easy to maintain and can be customized to suit individual preferences. Their modular nature makes them adaptable to different gardening styles.
- Containers: Ideal for balconies, patios, or small yards, container gardens allow you to grow vegetables in pots or other containers. This flexibility enables you to move your garden as needed and tailor it to specific plant requirements. Containers can be as simple or elaborate as you wish, making them accessible to a wide range of gardeners.
- In-Ground Gardens: For those with ample space and suitable soil conditions, in-ground gardens offer the opportunity to grow a wider variety of vegetables. This approach can result in a significant harvest if properly planned and managed. In-ground gardens often benefit from the natural fertility of the soil, but require more initial preparation.
Essential Tools and Materials
A well-stocked gardening toolkit is crucial for success. These tools will aid in every stage of your gardening journey.
- Gardening Gloves: Protect your hands from dirt, thorns, and other hazards.
- Shovels and Spades: Essential for digging, turning soil, and transplanting.
- Watering Can or Hose: Essential for consistent moisture.
- Gardening Trowel: Useful for planting, weeding, and other smaller tasks.
- Gardening Tools: Including hand rakes, hand cultivators, and a hoe to help maintain and till the soil. These tools allow for precise work, promoting healthy growth and optimal yields.
- Soil Amendments: Improving soil quality can significantly impact plant growth. Compost, fertilizer, and other amendments can enrich the soil, providing necessary nutrients for the plants.
Choosing the Right Location
Selecting a suitable location for your garden is key to achieving optimal growth. Factors such as sunlight, water availability, and soil conditions play critical roles.
- Sunlight: Many vegetables require at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight daily. Identify areas that receive ample sunlight to ensure healthy growth.
- Water Availability: Proximity to a water source is essential for consistent watering. A reliable water supply ensures the plants receive the necessary hydration.
- Soil Conditions: Assess the drainage and texture of the soil. Well-drained soil is crucial for preventing root rot. Observe the soil structure and composition.
Vegetable Selection and Growing Conditions
This table highlights suitable vegetable types for various growing conditions. Matching the vegetable with appropriate growing conditions is vital for success.
| Vegetable Type | Sunlight Requirements | Soil Type |
|---|---|---|
| Tomatoes | Full sun | Well-drained |
| Lettuce | Partial shade | Moist |
| Peppers | Full sun | Rich soil |
Planning and Design

A well-planned vegetable garden is crucial for successful harvests. Careful consideration of layout, soil quality, and plant selection ensures optimal growth and maximizes the yield. Proper planning saves time and effort in the long run, making the entire gardening experience more enjoyable and rewarding.Effective planning allows for efficient use of space, optimized plant spacing for healthy growth, and selection of vegetables suited to the available growing conditions.
This careful preparation significantly impacts the overall success of your home vegetable garden.
Garden Layout Planning
Careful planning of your garden layout is essential for efficient use of space and maximizing yield. A well-structured plan ensures that each plant receives adequate sunlight and water, minimizes competition between plants, and makes harvesting easier.A step-by-step guide to planning your garden layout includes:
- Site Assessment: Evaluate the available space, considering factors like sunlight exposure, soil type, and proximity to water sources. Note any existing obstacles, such as trees or structures, that may affect plant growth.
- Sunlight Analysis: Determine the hours of sunlight each area receives throughout the day. Vegetables have varying sunlight requirements. Sun-loving plants need at least six hours of direct sunlight, while shade-tolerant plants can thrive in areas with less sunlight.
- Soil Testing: Test the soil’s pH and nutrient levels. This information will guide your soil preparation efforts, ensuring the soil is conducive to the chosen vegetables.
- Plot Design: Sketch a rough plan of your garden layout, including the placement of different vegetable types. Consider factors like plant spacing and the potential for companion planting.
- Finalization and Implementation: Refine the plan, considering any necessary adjustments. Implement the plan, marking the plot boundaries and planting the seeds or seedlings according to the layout.
Vegetable Selection
Selecting the right vegetables is essential for a successful garden. Careful consideration of space requirements, growing seasons, and personal preferences are critical to a productive garden.Factors to consider when choosing vegetables include:
- Space Requirements: Different vegetables have different space needs. Some, like leafy greens, can be planted closely together, while others, like tomatoes or squash, need more space to grow and develop.
- Growing Seasons: Some vegetables, such as leafy greens, are suitable for multiple plantings throughout the growing season, while others, such as winter squash, have specific growing seasons.
- Personal Preferences: Choose vegetables you enjoy eating and that fit your culinary preferences.
Small Space Garden Layout
A simple garden layout for a small space could involve raised beds, maximizing vertical space. This allows for a variety of vegetables in a compact area. 
Example layout (Image): A rectangular raised bed divided into sections for different vegetables, such as lettuce, herbs, and small fruiting plants, with a vertical trellis for climbing vegetables.
Soil Preparation
Soil preparation is paramount for optimal plant growth. Improving the soil structure and nutrient content is crucial for successful gardening.Methods of soil improvement include:
- Adding Organic Matter: Incorporating compost, manure, or other organic matter enriches the soil with nutrients and improves its structure. This helps with water retention and aeration, benefiting plant roots.
- Amendments: Using amendments such as peat moss or vermiculite improves soil drainage and water retention.
- Testing and Adjusting pH: Testing the soil’s pH is crucial for identifying the need for adjustments. This may involve adding lime to increase the pH or sulfur to decrease it, depending on the specific requirements of the plants.
Container Comparison
Different containers offer various advantages and disadvantages for growing vegetables. Choosing the right container depends on your specific needs and gardening style.
| Container Type | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Raised Beds | Good drainage, customizable size and shape, can be built to specific needs. | Can be expensive, depending on size and materials, less mobile. |
| Pots | Mobile, easy to manage, adaptable to various spaces, allows for easier control of soil conditions. | Limited space compared to raised beds, may need more frequent watering. |
Sowing and Planting

Getting your home vegetable garden off the ground begins with sowing seeds and planting seedlings. Proper techniques for seed starting and transplanting are crucial for healthy growth and a bountiful harvest. This section details various methods, essential preparation steps, and optimal timing for a successful start to your gardening journey.
Seed Sowing Methods
Different vegetable types and personal preferences dictate the best seed starting method. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each method will help you choose the right approach for your needs. Direct sowing involves planting seeds directly into the garden bed, while starting seeds indoors allows for an earlier start, especially for plants with longer growing seasons.
- Direct Sowing: This straightforward method involves placing seeds directly into the prepared garden bed. It is often the simplest and most cost-effective approach, as it eliminates the need for additional containers and transplanting. However, it requires precise timing to ensure seeds germinate at the most opportune moment for the local climate. For example, if your region experiences late frosts, direct sowing might not be suitable for frost-sensitive plants.
- Starting Indoors: This method allows you to begin the growing process earlier in the season, often crucial for vegetables with longer maturation times. By starting seeds indoors in containers, you can control the environment and ensure optimal germination and growth before transplanting to the garden. This approach can also protect seedlings from harsh weather conditions and pests, boosting their survival rate.
Preparing Seedbeds and Containers
Proper preparation is key to successful germination and growth. The condition of the soil or container will greatly impact the outcome of the planting.
- Seedbeds: For direct sowing, the soil should be well-drained and loose, allowing for easy seed penetration and root development. Amend the soil with organic matter like compost to improve its structure and fertility. Level the surface to ensure a consistent planting depth.
- Containers: When starting seeds indoors, select appropriate containers. Containers should have drainage holes to prevent waterlogging. Use seed starting mix, which is a well-draining and nutrient-rich medium, ensuring optimal seed germination and growth.
Transplanting Seedlings
Transplanting seedlings is a critical step to ensure healthy growth. Carefully chosen methods will support the growth and survival of the seedlings.
- Procedure: Carefully remove the seedling from its container, being mindful not to damage the delicate root system. Dig a hole in the prepared garden bed that is slightly larger than the root ball. Gently place the seedling in the hole, ensuring the roots are spread out evenly. Backfill the hole with soil, firming gently around the roots to eliminate air pockets.
Water thoroughly after transplanting to settle the soil and provide moisture.
Optimal Sowing Time
Timing is essential for successful seed germination. Understanding the local climate and specific plant requirements is crucial. For example, in regions with short growing seasons, starting seeds indoors will give a head start for some plants.
- Considerations: Research the specific sowing time for each vegetable variety, considering factors such as the average last frost date, the length of the growing season, and the plant’s maturity time. This knowledge will guide your decision on the most appropriate sowing time for each plant type.
Maintaining Soil Moisture
Consistent moisture is vital for seedling growth. Regular monitoring and appropriate watering techniques are essential for healthy plant development.
- Techniques: Water regularly, ensuring the soil stays consistently moist but not waterlogged. Mulching around seedlings helps retain moisture and regulate soil temperature. Water deeply but less frequently to encourage deeper root growth. Monitoring soil moisture using your finger or a moisture meter will help you determine when to water. Avoid overhead watering, as it can lead to fungal diseases.
Instead, water at the base of the plants to minimize water loss through evaporation.
Seed Starting Methods Comparison
| Method | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Sowing | Simple, cost-effective, reduces handling | Requires precise timing, potential for late germination |
| Starting Indoors | Allows for early planting, protects from harsh weather | More time-consuming, requires containers and additional care |
Care and Maintenance
Proper care and maintenance are crucial for successful home vegetable gardening. Consistent attention to watering, fertilization, and pest control ensures healthy plant growth and abundant harvests. Neglecting these aspects can lead to stunted growth, disease outbreaks, and ultimately, reduced yields. By understanding and implementing the appropriate techniques, gardeners can cultivate thriving vegetable gardens that provide fresh, homegrown produce.
Watering Techniques
Effective watering is essential for healthy plant development. Overwatering or underwatering can severely impact plant health. The ideal approach is to water deeply and less frequently, encouraging roots to grow deeper into the soil. This method promotes stronger, more resilient plants. Water at the base of the plants, avoiding wetting the foliage to minimize the risk of fungal diseases.
Observe the soil moisture regularly and adjust the watering schedule based on weather conditions and plant needs. Consider using soaker hoses or drip irrigation systems for efficient and targeted watering. These methods deliver water directly to the roots, reducing water waste and promoting healthier plant growth.
Fertilization Practices
Regular fertilization provides essential nutrients for vigorous plant growth. Different vegetables have varying nutritional requirements, so understanding the specific needs of each plant is important. A balanced fertilizer with nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium is often sufficient. Applying too much fertilizer can harm the plants, so follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. Organic fertilizers, derived from natural sources like compost or manure, are often preferred for their gradual release of nutrients and positive impact on soil health.
Incorporating organic matter into the soil, such as compost or well-rotted manure, also enhances soil fertility and reduces the need for synthetic fertilizers.
Pest and Disease Control
Maintaining a healthy vegetable garden involves proactive pest and disease control. Regular inspection of plants is vital for early detection of potential problems. Observe for signs of insects, such as chewing or sucking damage, and diseases, such as spots or wilting. Implement appropriate pest control measures early to prevent widespread infestations. Organic methods, such as introducing beneficial insects or using natural pest repellents, can be effective and environmentally friendly.
However, if necessary, consider using conventional pesticides according to the label instructions. Remember to practice proper safety precautions when handling pesticides.
Monitoring Plant Growth
Regularly monitoring plant growth allows gardeners to identify potential problems early on. This includes checking for signs of stress, such as yellowing leaves or stunted growth. Examine the plants for any signs of pest damage or disease symptoms. By closely observing the plants, gardeners can intervene promptly and prevent serious issues. Note any unusual patterns in plant development and promptly address any concerns to maintain healthy growth.
Common Plant Diseases and Remedies
A table outlining common vegetable plant diseases and their remedies is provided below.
| Disease | Symptoms | Remedies |
|---|---|---|
| Damping-off | Seedlings collapse and die | Improve soil drainage, use disease-resistant seeds, avoid overhead watering. |
| Blight | Spots or lesions on leaves and stems | Remove affected plant parts, use fungicides if necessary, maintain good air circulation. |
| Powdery mildew | White powdery coating on leaves | Increase air circulation, remove affected leaves, apply a suitable fungicide. |
| Root rot | Wilting, yellowing, and stunted growth | Improve soil drainage, avoid overwatering, use well-draining soil mix. |
Harvesting and Storage
Harvesting and storage are crucial steps in home vegetable gardening. Proper techniques ensure the best quality and longevity of your produce. Timing and method are key to maximizing the harvest’s freshness and preserving its nutritional value. Understanding the optimal harvest time for each vegetable, along with suitable storage methods, will significantly extend the enjoyment of your homegrown bounty.
Optimal Harvest Times
Different vegetables have specific ideal harvest times, directly influencing their quality and flavor. Knowing when to harvest maximizes taste and texture. For example, beans should be picked when pods are plump and vibrant, while tomatoes should be harvested when they have reached their desired color and firmness. The timing of harvesting is often dependent on the variety and the specific growing conditions.
Proper Harvesting Techniques
Using appropriate techniques prevents damage to the vegetables and maintains their quality. Carefully handling produce minimizes bruising and breakage. Avoid pulling or twisting vegetables; instead, use a sharp knife or pruning shears to cut them from the plant. This will maintain the integrity of the plant for future harvests.
Storage Methods
Numerous methods exist for preserving harvested vegetables. Proper storage extends shelf life and maintains the quality of your harvest. Storing vegetables in the refrigerator, freezing them, or using methods like pickling, drying, or root cellars can significantly prolong their lifespan. Choosing the right method depends on the type of vegetable and your desired storage duration.
Extending Shelf Life
Several strategies can be used to prolong the freshness of your harvest. Proper storage conditions are paramount in extending the life of your produce. For example, storing leafy greens in a cool, humid environment can help prevent wilting. Vegetables like tomatoes and peppers benefit from being stored at room temperature. These measures can significantly extend the shelf life of your homegrown harvest.
Cleaning and Preparation for Storage
Thorough cleaning and preparation before storage is vital. Cleaning vegetables removes dirt and debris, preventing spoilage. Washing vegetables gently and carefully is crucial to avoid damaging them. Then, dry them completely to prevent mold growth. This thorough process is vital for preserving quality and extending shelf life.
Flowchart: Harvesting and Storage
 (Note: This is a placeholder for a visual flowchart. The flowchart should visually depict the steps for harvesting and storing various vegetables, guiding users through the process based on the specific vegetable type. For example, it would have branches for root vegetables, leafy greens, fruits, etc.)The flowchart would Artikel the following general steps:
(Note: This is a placeholder for a visual flowchart. The flowchart should visually depict the steps for harvesting and storing various vegetables, guiding users through the process based on the specific vegetable type. For example, it would have branches for root vegetables, leafy greens, fruits, etc.)The flowchart would Artikel the following general steps:
- Identify the vegetable: Determine the type of vegetable being harvested.
- Determine the optimal harvest time: Based on the vegetable type, check for ripeness and desired characteristics.
- Harvest the vegetable: Use appropriate tools and techniques to harvest without damaging the vegetable or plant.
- Clean the vegetable: Thoroughly wash and dry the vegetable.
- Select the appropriate storage method: Decide whether to store in the refrigerator, freezer, or other methods like drying or pickling.
- Store the vegetable: Place the vegetable in the chosen storage container or environment.
- Monitor and maintain: Regularly check the storage conditions and adjust as needed to maintain quality.
Troubleshooting
Maintaining a thriving home vegetable garden requires proactive problem-solving. Understanding common issues and their solutions allows you to address problems quickly, preventing further damage and maximizing your harvest. This section details troubleshooting strategies for various garden challenges.Identifying the cause of a problem is crucial before applying a solution. Careful observation of the affected plants, including their surroundings, is key.
Common Vegetable Problems and Their Causes
A systematic approach to identifying plant issues is essential. Understanding the possible causes for various problems is a critical step towards successful problem resolution. The table below provides a concise overview of potential problems and their probable causes, helping you determine the root of the issue.
| Problem | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Yellowing leaves | Nutrient deficiency (e.g., nitrogen, iron), overwatering, or underwatering | Apply a balanced fertilizer appropriate for the specific nutrient deficiency, adjust watering schedule, ensuring proper soil moisture. |
| Wilting plants | Lack of water, extreme heat, or pest infestation | Water deeply and regularly, especially during hot periods. Check for signs of pests and implement appropriate control measures. |
| Slow growth | Nutrient deficiencies, compacted soil, or inadequate sunlight | Amend the soil with compost or other organic matter to improve drainage and aeration. Ensure the plants receive adequate sunlight based on their specific needs. Consider fertilizer application. |
| Sudden leaf drop | Pest infestation, disease, extreme temperatures, or improper watering | Inspect for pests and diseases. Adjust watering to prevent over or underwatering. Protect plants from harsh weather conditions. |
| Root rot | Overwatering, poor drainage, or fungal pathogens | Reduce watering frequency, improve soil drainage, and apply fungicides as needed. |
Pest and Disease Identification
Recognizing common pests and diseases affecting vegetables is vital for effective management. Identifying these issues early allows for timely intervention and prevents widespread damage.
- Aphids: Small, sap-sucking insects. Look for clusters of small, soft-bodied insects on leaves or stems. They can be controlled by introducing beneficial insects or insecticidal soaps.
- Spider mites: Tiny pests that create webbing on leaves. Leaves may appear yellow or have stippled damage. Treat with insecticidal soap or horticultural oil.
- Fungal diseases: Diseases like powdery mildew and blight can cause white or dark spots on leaves, or overall leaf discoloration. Use fungicides and improve air circulation around plants to prevent their spread.
- Root knot nematodes: Tiny worms that infest roots. Affected plants exhibit stunted growth and yellowing leaves. Amend soil with organic matter and consider resistant plant varieties.
Diagnosing Plant Issues
Careful observation of the affected plant is paramount in determining the underlying cause. Examine the leaves, stems, roots, and surrounding soil for clues. Look for signs of pests (e.g., small insects, webs, or droppings), wilting, yellowing, or unusual discoloration.
Further Considerations
- Environmental Factors: Extreme weather conditions (heat, frost, drought) can stress plants and lead to various problems. Providing appropriate shelter or adjusting watering schedules can mitigate these issues.
- Soil Conditions: Poor soil drainage, compaction, or pH imbalances can affect plant health. Testing the soil and amending it with organic matter can improve these conditions.
- Plant Variety: Some plant varieties are more susceptible to certain pests or diseases than others. Choose disease-resistant varieties whenever possible.
Conclusive Thoughts

In conclusion, growing your own vegetables at home is an achievable goal for everyone. By carefully planning your garden, understanding the needs of different plants, and maintaining consistent care, you can enjoy a bountiful harvest. This guide offers a roadmap to help you overcome challenges, ensuring your home garden thrives. Embrace the satisfaction of growing your own food and the unique connection with nature.